Bitcoin is currently the world’s largest, oldest and most famous crypto currency. The idea for Bitcoin goes back to Satoshi Nakamoto, whose identity has not yet been clarified. There will be a maximum of only 21 million Bitcoins.
Quick Facts
Ticker Symbol: BTC
Max Number of Coins: 21 Million
Protocol: Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Table of Contents
Historical background to Bitcoin
The original domain Bitcoin.org was already registered on August 18, 2008. It was not until two and a half months later that the white paper on Bitcoin was published. A certain Satoshi Nakamoto published it with the title: “A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. The work on it began in 2007, however, and Satoshi Nakamoto’s identity has not yet been clarified. It is also not possible to trace back who registered the domain, because the registrar used the service of anonymousspeech.com, where everybody can register domains anonymously.
Interestingly, the domain Bitcoin.com was already registered in January 2008. However, it was registered by a technology company that has nothing to do with the crypto currency Bitcoin. Bitcoin.com is now owned by Roger Ver, who was later one of the initiators of Bitcoin Cash. He now uses the domain mainly to promote Bitcoin Cash.
In January 2009 the Bitcoin software and code was released. This was accompanied by the Bitcoin Blockchain going live on January 3, 2009 and the first block being mined. This first block at Bitcoin is called Genesis Block. This first block also contains a short sentence, literally the block says: “The Times 03/Jan/2019 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks”. The text is from a Times article (the Times from London) published on that day. It is believed that Satoshi Nakamoto took this headline to criticize the existing banking system that collapsed in 2008.
The first Bitcoin transaction was received by Cypherpunk Hal Finney. He has already downloaded the software on the day of the release. On January 12, 2009 he received the first 10 Bitcoins from Satoshi Nakamoto. Other early supporters of Bitcoin were Like Dai and Nick Szabo, who developed his own digital crypto currency, Bit Gold, which was never implemented.
It took until 2010 for the first commercial transaction to take place at Bitcoin. At that time Laszlo Hanyecz bought two Papa John’s Pizza for 10,000 Bitcoins. The story started with him writing a post to the Bitcointalk Forum. There he asked who would deliver him 2 pizzas for 10.000 Bitcoins. Only 4 days later someone was found who accepted the order. The 10,000 Bitcoins were worth 42 US dollars at the time. Anyone can figure out what they’re worth now.
Bitcoin found further acceptance in 2011 with the black market Silk Road. On the marketplace, mainly drugs were sold. Bitcoin was used as an anonymous means of payment. Silk Road existed for almost 30 months. During this time, a total of 9.9 million Bitcoins were transferred on the marketplace. In 2011 Litecoin was also created as Bitcoin Hard Fork. The little brother of Bitcoin, as Litecoin is often referred to, implemented many technologies before they came to Bitcoin.
In September 2012 the Bitcoin Foundation was established. Its mission is to make Bitcoin better known and to further the development of Bitcoin. At that time, however, Satoshi Nakamoto was no longer an active member of the Bitcoin community and his involvement ended at the end of 2010, by which time he had passed on all important tasks to other developers. Gavin Andresen received the Network Alert Key from Satoshi Nakamoto. Satoshi Nakamoto has also given domains to prominent members of the Bitcoin community.
The Mt. Gox Hack
The Japanese Bitcoin Exchange Mt. Gox was already founded in July 2010. This became the most popular crypto exchange worldwide within a very short time. In the end, however, the Exchange broke down because it was allegedly hacked in February 2014. At that time, almost 850,000 Bitcoins are said to have been stolen. How significant this event was is shown by the fact that over 70% of the worldwide Bitcoin trade took place on Mt.
To this day it is not clear whether there really was a hack. Many people believe that the management was behind the hacker attack and that they themselves had embezzled the Bitcoins. In the end, 200,000 Bitcoins were found in cold wallets at Mt. Gox. These were distributed by the Japanese insolvency administrator to the then aggrieved parties. Due to the increase in value of Bitcoin, investors’ losses in euros or dollars are naturally limited, only in Bitcoin have investors lost a lot.
But Mt. Gox was not the only hack of a crypto exchange – other exchanges have also fallen victim to hackers. Another known victim is Bitfinex also here there was a hack in 2016 where Bitcoins worth 72 million US dollars were stolen. In addition to Bitfinex, Coincheck, Coinrail and Bithumb were later also caught.
Who is Satoshi Nakamoto?
Until today it is not clear who exactly is hiding behind the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It is certain, however, that it must be someone who has (or the) profound knowledge in cryptography and is also a computer expert. Some also assume that Satoshi Nakamoto is not a single person, but a group of people. Apart from that, there are some people who are always mentioned when it comes to who Satoshi Nakamoto is. Here are the most important ones:

Hal Finney
He was with Bitcoin from day one and also received the first transaction from Satoshi Nakamoto. In addition, an analysis of his texts has shown that they are very similar in wording to those of Satoshi Nakamoto. In addition, he lived in the same city as Dorian Satoshi Nakamoto (Temple City California) for 10 years. But Hal Finney denied to be Satoshi Nakamoto and also tried to present evidence that he is not. Hal Finney died on August 28, 2014. The death did not come as a surprise because already the year before his body failed so badly that he could only move around in a wheelchair.
Nick Szabo
Also a candidate to be Satoshi Nakamoto is Nick Szabo. He introduced the concept of the digital crypto currency Bit Gold before Bitcoin and was also involved in Bitcoin from the beginning. The New York Times author Nathaniel Popper on the other hand writes Compared to others, the most compelling evidence suggests that Nick Szabo is Satoshi Nakamoto. But Nick Szabo also denies to be Nakamoto and there is no really conclusive evidence for this either.
Dorian Nakamoto

He was identified as Satoshi Nakamoto in a Newsweek article on March 6, 2014; after all, his birth name is Satoshi Nakamoto. The studied physicist has already worked in the past as a computer engineer for a financial company. Furthermore, he has very similar liberal views as Satoshi Nakamoto. However, many consider it impossible that Dorian Nakamoto is also the inventor of Bitcoin. Because the real Satoshi Nakamoto has done a lot to remain anonymous (e.g. anonymous website registration), why would he give his birth name as a pseudonym.
Craig Wright

To anticipate it Craig Wright is certainly not Satoshi Nakamoto even though he claimed the Wired in an article on December 8, 2015. Meanwhile Craig Wright himself claims that he is Satoshi Nakamoto. However, he has not yet managed to present credible evidence for this. Furthermore, there are many statements from him that show that he does not understand crypto currencies nearly as well as the real Satoshi Nakamoto. Many in the crypto scene therefore call Craig Wright Faketoshi. A detailed list of all reasons why Craig Wright cannot be Satoshi Nakamoto can be found here.
Besides these 4 candidates there are other names that appear from time to time like Gavin Andresen, Jed Mccaleb (co-founder of Stellar and Ripple), Joshua Davis and others. But so far there is no concrete evidence that any of the mentioned ones is really Satoshi Nakamoto.
Which means that one of the named candidates could clearly prove that he is Satoshi Nakamoto if he moves Bitcoins that are assigned to Satoshi Nakamoto. This is because most of the Bitcoins in the beginning were mined by Satoshi Nakamoto himself. It can be assumed that Satoshi Nakamoto himself owns nearly 1 million Bitcoins. But these have not been moved on the Blockchain until today and thus have not been sold. In December 2017, the Bitcoins were worth 20 billion US dollars in the meantime. If Hal Finney Satoshi Nakamoto would be then it is to be assumed that the Private Keys disappeared forever by his death.
Besides Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto was also the initiator of the Bitcointalk Forum. Until today the Bitcointalk Forum is one of the places where enthusiasts exchange information about Bitcoin and Co.
Technical implementation of Bitcoin
Bitcoin is based on the Blockchain technology. This is a kind of public cash ledger. Miners are constantly looking for new blocks for this ledger (the block chain). With Bitcoin, a new block is found every 10 minutes on average. This is then attached to the block chain. Each block has an integrated SHA-256 hash that refers to the previous block. Therefore the order of the block chain cannot be changed. All transactions that have taken place since the last block are then confirmed in a block.
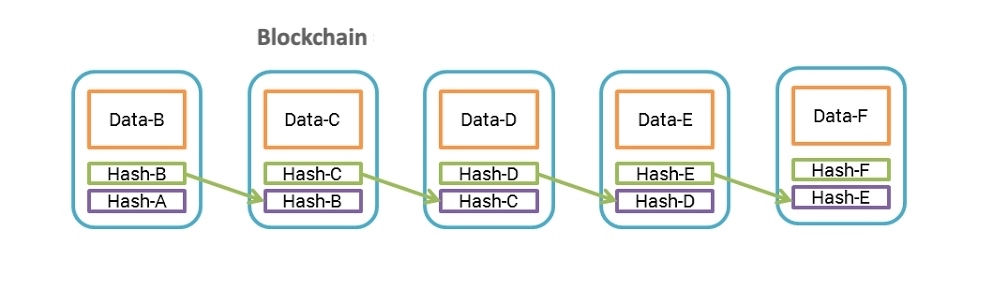
Unlike a database stored on a computer, the Bitcoin block chain is stored on so-called nodes. Basically anyone can operate a Bitcoin node on the Internet. Each node has the complete Bitcoin block chain stored. The nodes are synchronized with each other, which ensures that they all always have the current state of the Bitcoin network stored.
Due to the system of nodes, Bitcoin is a decentralized system. It is not managed or controlled by a central instance. However, decentralized systems such as Bitcoin have the disadvantage that they are much slower than centralized systems. This is due to the fact that the majority of the network must first confirm the transaction in question. Bitcoin payments therefore do not really take place without time delay, as only a part of the network has to confirm the respective payment.
Further development of Bitcoin
The software code for Bitcoin is constantly being improved. This is also necessary because time and again errors are found in the code that need to be corrected. In addition, the technical development of the Miners and Wallets continues.
For the further development of Bitcoin, so-called Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIP) were introduced. The first Bitcoin Improvement Proposal was BIP 0001 and was submitted by Amir Taaki on August 19, 2011. The proposal was about the introduction of BIPs to update Bitcoin. This proposal was adopted by the Bitcoin community and the system is now well established.
There are basically 3 types of Bitcoin Improvement proposals (BIPs):
- Standard Track BIPs: These are proposals to change the network protocol, block or transaction validations or anything else that affects the way Bitcoin works.
- Informational BIPs: This variant is about improving design guidelines or general guidelines.
- Process BIPs: These are proposals to change processes.
Basically, any submitted Bitcoin Improvement Proposal can only be either accepted, rejected or withdrawn. Accepted proposals are then implemented by the community.
Private and Public Keys
Bitcoin credits are always stored on the block chain and remain there. Bitcoin credits basically consist of a Private Key and a Public Key. As the name suggests, the Public Key is a public key that indicates where the credits are stored on the block chain. The Public Key can be compared to an account number, behind which credits are hidden. In comparison to a bank account, however, it is usually not clear who owns these credit balances with a public key. While a bank account is assigned to a name, Bitcoin Wallet addresses are anonymous.
The Bitcoin Public Key is often referred to as a Wallet address. To receive Bitcoins, you must give the sender your Bitcoin address (i.e. the public key or wallet address).
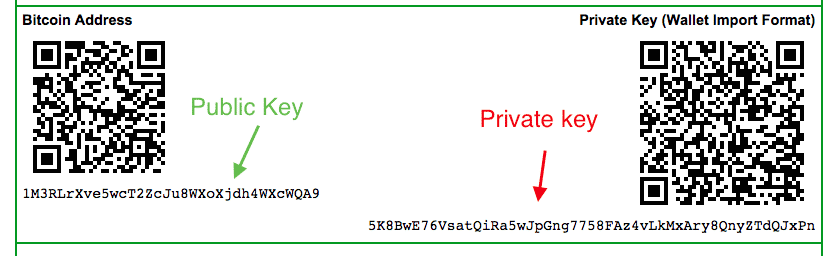
In addition to the public key there is also a private key (secret key). With this one gets access to the credits. Everyone who has the private key controls the credit balance. In order to transfer the credits, the private key is sufficient, because the public key can be generated from every private key. The other way round is of course not possible.
Anyone who has stored Bitcoin on an exchange is usually not in possession of the private key. Here the exchange (crypto exchange) takes over the storage of the credit. However, the credit can also be easily withdrawn from most Exchanges.
Bitcoin Mining
In principle, anyone can mine Bitcoins with their computer. This was also very effective in the beginning of Bitcoin. In the meantime there are special mining hardware (ASIC Miner), which is optimized to mine Bitcoins. This hardware is much more efficient than a normal computer. While the mining hardware is also available for normal consumers, it might be difficult for private persons to buy electricity as cheaply as professional mining companies. Many miners pay hardly more than 0.04 – 0.06 Euro per kilowatt hour. That is also the main reason why there are hardly any private individuals left who mine Bitcoin.

Mining uses computing power to find the next block. Finding the block is based on the random principle but the more computing power you have the more likely you are to find a block. The miner who found a block will be credited with the block rewards. These are a fixed number of Bitcoins that are paid out as an incentive for mining. These Block Rewards decrease every few years. In addition to the Block Rewards, each Miner also receives the transaction fees from all transactions that are written into the Block Rewards and thus confirmed. The block is then attached to the block chain.
On average, Bitcoin finds a new block every 10 minutes. This value is preset. However, as more and more computing power is available in the Bitcoin network, the time until the next block is found should actually become shorter and shorter. To prevent this from happening there is an adjustment of the mining difficulty every 2,016 blocks (about every 14 days). So if more miners are added to the network and therefore more computing power is available, the Mining Difficulty is increased. The same principle also applies if miners disappear from the network, then the Mining Difficulty is reduced. This ensures that even in the long term a new block is found only every 10 minutes.
Bitcoin Mining is also called Proof-of-Work (PoW). In other words, if you want to get Bitcoins, you have to provide work (computing power). Because there are now so many miners, the Bitcoin network is also relatively secure. If there weren’t so many miners, large miners could simply rewrite the block chain as they wish, because after all, they decide which transactions get into the blocks. To do this they would have to control 51% of the mining performance in the network. This is no longer possible with Bitcoin using individual miners. Nevertheless, there is criticism that the majority of the miners are controlled by Chinese companies. The majority of Bitcoin’s mining capacity is provided by only a handful of companies. Especially with smaller crypto currencies there have been numerous cases in the past where these 51% attacks were successfully carried out.
Transactions with Bitcoin
To carry out a transaction at Bitcoin, you need the public address (also called public key) of the recipient. A transaction can only be carried out with this address alone. The transaction is then written to the next free block and confirmed by the nodes. Usually a transaction is immediately visible on the block chain. However, it then takes some time until a large part of the network has confirmed the transaction. Only when the transaction has been confirmed by the majority of the network, the user can use the received credits and, for example, forward them.
Bitcoin transactions are limited to the block size. As we have already seen above, a new block is only found on Bitcoin every 10 minutes on average. The maximum size of a block is 1 MB: This means that only so many transactions can be written to the block until the 1 MB limit is reached. As a result, Bitcoin can currently only handle a maximum of 7 transactions per second. For comparison, the credit card company Visa processes about 4,000 transactions per second, but can also process up to 65,000 transactions per second. The limited number of transactions is the biggest problem in scaling Bitcoin.
The cost of a transaction at Bitcoin depends heavily on how many transactions are currently being processed in the network. Basically the miners decide which transactions they write to the blocks they have found. Since the Miners receive the transaction fees they naturally have an incentive to keep the transaction fees as high as possible. So if there are more transactions than could be theoretically confirmed, the miners can choose which transactions they write into the block. As a rule, the transactions with the highest fees will be the ones with the highest transaction fees.
In December 2017 there was a situation where so many Bitcoin transactions were made that it cost 55 US dollars to send Bitcoins to another address. In the meantime the situation has normalized and a Bitcoin transaction costs less than 0.25 US dollars.
Important to know with Bitcoin transactions is that the transaction fees are dependent on the number of Bitcoins you send. So whether you send 1 or 1,000 Bitcoins in a transaction, the fees should be the same in both cases.
Units with Bitcoin
In total, there will be a maximum of almost 21 million Bitcoins (20,999,999,9769 to be precise). Although different units in Bitcoin have different names, only Bitcoins and Satoshi are really used. Bitcoin can be broken down to the 8th decimal place. The 8th decimal place and thus the smallest unit in Bitcoin is called Satoshi. All other designations are then as follows:
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Lightning Netzwerk
As mentioned above, one of the biggest problems with Bitcoin is that it can only handle a maximum of 7 transactions per second. The problem of limited scalability in Bitcoin is to be solved in the long term with the help of the Lightning network. The Lightning network is already live and ready to be used.
The idea behind the Lightning network is that not all transactions have to take place on the block chain and should be written into it. Especially for smaller amounts it is also possible to carry out transactions “off-chain”, i.e. outside the block chain. In this case, so-called payment channels are opened between the sender and the recipient. In these payment channels you can then carry out transactions as often as you like. Compared to block chain transactions, the transactions take place immediately. Only when the payment channel is closed is an entry made on the block chain. In the entry is then recorded what the new credit of the recipient and sender is. Credit can be sent not only via direct payment channels, but also via indirect ones. So I don’t necessarily have to have a direct payment channel to the recipient, but the payment can also be forwarded via a third or fourth person to whom I have a payment channel and who then has a payment channel to the recipient.
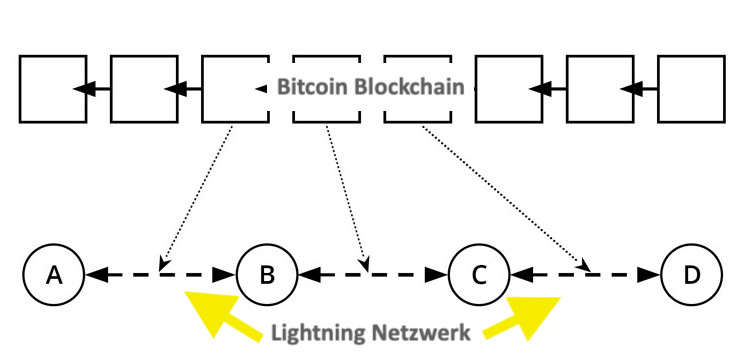
In addition to the faster processing of transactions, the Lightning network also makes them significantly cheaper and the fees can easily be less than 0.01 euros. In theory, the Lightning network is scalable to any size and can easily handle millions of transactions per second.
So let’s say that the idea at Bitcoin is to leave large transactions on the block chain and to do small transactions, like buying a coffee, on the Lightning network.
To conduct transactions on the Lightning network you need a wallet that supports the Lightning network. On the desktop this can be the Lightning app, but also for iOS and Android there is a special app for this purpose, the Blue Wallet.
Criticism of Bitcoin
Although there are many advantages of the crypto currency Bitcoin, there is also occasional criticism of Bitcoin. There are especially 3 major points of criticism:
1. Volatility: Bitcoin is often seen as an alternative store of value. Especially in countries with very high inflation (e.g. Venezuela) Bitcoin can be a real alternative. However, the price of Bitcoin is not yet so stable that it makes sense for the majority of people to use Bitcoin. Especially between the end of December 2017 and December 2018 we could observe how Bitcoin fell from 20,000 US dollars to almost 3,000 US dollars. These strong fluctuations in the exchange rate naturally deter many from investing large sums in Bitcoin.
2. Scalability: We already mentioned that Bitcoin currently only allows 7 transactions per second on average. But if we look at the fact that Visa currently processes 4,000 transactions per second and can afford a multiple of that, it is easy to see that Bitcoin is currently not suitable as a normal means of payment. However, since Bitcoin is not a rigid system, but rather the crypto currency is continuously being developed, it can be assumed that the problem of scalability is only a short-term one. A possible solution is already live with the Lightning network.
3. Energy Consumption: Since Bitcoin relies on the so-called proof-of-work algorithm, the network is dependent on miners. However, the mining of Bitcoin is very energy-intensive. There are studies that say that Bitcoin consumes more energy per year than the whole of Austria. However, it should also be noted that a good 70% of the energy used for Bitcoin mining comes from sustainable energy sources. For example, many miners are located in Iceland and operate their mining farms using geothermal energy. So even though Bitcoin mining is energy-intensive, the miners still strive to use sustainable resources. Fossil fuels are also often too expensive to use for Bitcoin mining.
Buying and selling Bitcoins
If you want to buy Bitcoins you have to do this at a so-called crypto exchange. We recommend eToro for this. If eToro is not available in your country you can also use Coinbase. Both platforms have fair fees and you can buy Bitcoins in Fiat currency.
Bitcoin Wallets
If you do not want to leave your Bitcoins on a crypto exchange, you can also withdraw them and store them on your own wallet. In general, it is safer to manage your crypto credit yourself – the safest way is to use a hardware wallet. The stock exchanges do a lot to protect them from hacker attacks, but it is never quite safe. In the past we have seen with the Mt. Gox (2014) and the Bitfinex (2016) hack that even large exchanges do not offer 100% protection.
To store your Bitcoins you have 4 options. These differ as follows.
1. Bitcoin Paper Wallets: As the name suggests, your credits are stored on a sheet of paper. Actually, only the Private Key is printed on the paper. If you have the Private Key, you have access to the entire credit balance and can transfer it. A Paper Wallet looks something like this.
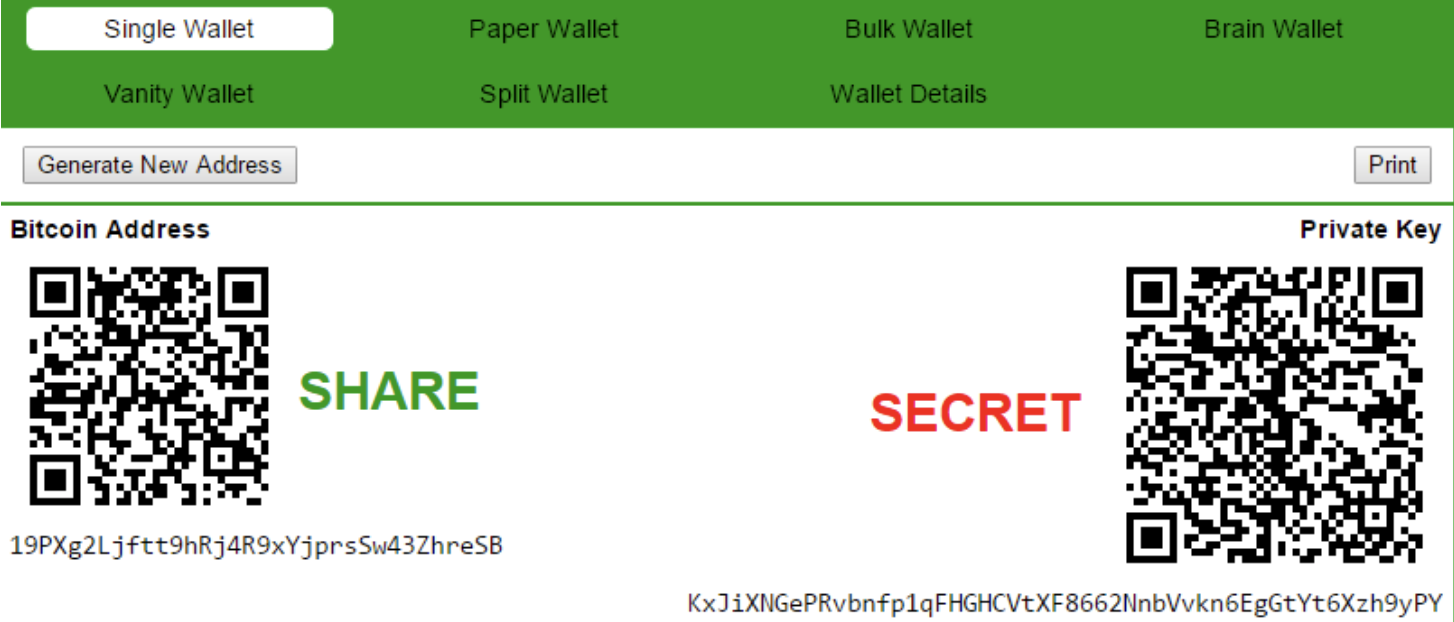
For the creation of these Paper Wallets there are several websites that support you. The best known service for Paper Wallets is bitaddress.org. The site is also available offline, so you don’t have to be online to create a Paper Wallet (recommended). It is also important that you store your Paper Wallet in a way that it is protected in case of fire and burglars should not be able to find it. How much effort you put into this depends on how much credit is on the individual Wallet.
2. Software Wallets: In addition to the paper wallet there are of course also the normal software wallets. You simply install them on your computer or smartphone and can send or receive credits. The Software Wallets on your computer are called Full Client and Light Client. The Full Clients store the entire block chain. Due to the size of the Bitcoin block chain (more than 200GB of storage space required) we would advise you not to use a Full Client. This also includes a complete Bitcoin Full Node. If you want to try it, you should try the Bitcoin Core Wallet. It is much easier to use a Light Client because it requires very little disk space. The most popular Light Client Software Wallet is Electrum. The Wallet is available for all platforms (MacOS, Windows, Linux). There are also wallets for mobile phones which you can use normally on your smartphone. Especially recommended is the ArcBit Wallet, which is available for iOS and Android.
3. Web Wallet: There are also websites where you can save your credit. These work as a kind of web wallet. However, this variant is hardly more secure than leaving your crypto credits on an exchange. If you want to try it anyway, we recommend BTC.com.
4. Hardware Wallet: The most secure way to store your crypto credit is with a hardware wallet. Market leader in hardware wallets is the French company Ledger with its Ledger Nano S and Ledger Nano X.
The special thing about a hardware wallet is that the private keys always remain on the wallet. Only the transactions are signed, so that nobody can steal the private keys. Even if you lose the hardware wallet, your credit won’t be gone because with the recovery key (consisting of 24 words) you can always restore it. On the ledger you can not only store Bitcoins, but also over 1.000 different crypto currencies.
Bitcoin Rate and Current Price
Links
Here we summarize once again the most important links for you. With the Block Explorer you have the possibility to track transactions and see how much credit is hidden behind a Bitcoin address.
Block Explorer: BlockExplorer.com
Website: Bitcoin.org
Exchange: eToro.com