IOTA is a platform with a crypto currency of the same name, which is not based on a classic block chain, but on the Tangle network. The application area of IOTA shall be mainly the Internet of Things (IoT). Unlike most other crypto-currencies, IOTA does not charge any fees for transactions, only two other transactions have to be confirmed.
Quick Facts
Ticker Symbol: MIOTA (sometimes also IOTA)
Maximum number: 2,779,530,283 MIOTA
Protocol: Proof of Work (PoW)
Table of Contents
Historical Background of IOTA

IOTA was already founded in 2015 by founder David Sønstebø, Sergey Ivancheglo, Dominik Schiener and Serguei Popov.
Naming
The name IOTA comes from the Greek alphabet and describes the 9th letter. The word IOTA is often used to describe a very small unit. This is exactly where the idea of IOTA comes in. Because the platform is primarily intended to enable data exchange between machines in the Internet of Things.
It is estimated that in the next few years we will have over 50 billion devices connected to the Internet. IOTA should become the standard in the Internet of Things and the devices should be able to communicate with each other using IOTA technology.
The ICO
In order to finance the project, IOTA conducted an ICO between 24 November and 20 December 2015. Investors had the opportunity to purchase IOTA Tokens (which were later distributed). Bitcoin was accepted as a means of payment. IOTA has raised almost half a million US dollars in Bitcoin through the ICO. This value always fluctuates slightly depending on the source, which is mainly due to the fact that the value of Bitcoin has risen from 330 US dollars to over 450 US dollars in this period.
What was special about the ICO was that there was no pre-mining as with Ethereum. There, the founders had obtained tokens for themselves before the ICO. The IOTA founders and the developers had to buy their own IOTA tokens. The value of a MIOTA (1 million IOTA) at that time was 0.001 US Dollar. Also special about IOTA is that there is a fixed amount of IOTA Token (2.779.530.283.277.761). This was created once and there will never be IOTA again. Generally important to know is that IOTA can be broken down into very small units. Therefore it is often said that MIOTA is 1 million IOTA. So if there is a price for IOTA of 0,30 US Dollar somewhere, this means always 1 MIOTA. It would make little sense to indicate the price of a single IOTA, because it would be 0.000000…. Therefore it is common to speak of MIOTA and these are nevertheless often called IOTA (by mistake).
Only after the IOTA ICO the investors could claim their IOTA tokens for themselves. As a result, on November 27, 2016 (almost 1 year after the start of the ICO) only 48% of all IOTA Tokens were claimed by investors. At that time there were 472 wallet addresses with credit. The number of ICO investors was therefore manageable. On February 4, 2017 60% of all IOTA were already distributed to ICO investors and the number of addresses increased to 657. To this day it is not clear how many IOTA ICO investors have never redeemed their tokens. The not redeemed tokens have then migrated to the foundation. There are theories that the two wallets with the largest balances belong to the IOTA Foundation and that these are the unredeemed balances. This would mean that 14.6% of all tokens were not redeemed by the ICO investors.
IOTA Ecosystem
In May 2017, IOTA announced that they were planning the IOTA Ecosystem. This is a focal point where all activities around IOTA will be bundled. In addition, there is also a fund to finance projects around the IOTA ecosystem. It took 1 year until the website went live and only then the first projects were financed.
Exchange Listing
On 13 June 2017, IOTA was listed for the first time on an exchange. IOTA was then listed at Bitfinex, where the crypto currency is still listed today. Previously IOTA was only traded among users. Often this was done through forums, especially Bitcoin Talk.
The dispute with the Digital Currency Initiative (DCI)
In the summer of 2017, IOTA has also attracted attention mainly due to a dispute with the Digital Currency Initiative (DCI). The whole event starts already in May 2017. At that time IOTA asked DCI to find weaknesses in IOTA. In July IOTA gets a first reaction. Ethan Heilman approaches IOTA and says that they have found several vulnerabilities. He specifically mentions the curl function that IOTA uses to encrypt signatures. How exactly such an attack can look like DCI does not reveal. IOTA reacts anyway and replaces the curl encryption with the more respected Keccak encryption. This could have been the end of the incident, but it is not. In September, DCI finally publishes a report with the lurid title: “IOTA Vulnerability Report: Cryptanalysis of the Curl Hash Function Enabling Practical Signature Forgery Attacks on the IOTA Cryptocurrency”.
At that time, curl was no longer used by IOTA. So in fact IOTA was no longer vulnerable. Nevertheless the report gives the impression that IOTA still has weaknesses. The report has caused a lot of attention and made IOTA look bad. As a result, nasty insults via email went back and forth between IOTA and DCI. IOTA accuses DCI especially Ethan Heilman that he has his own interest in making IOTA look bad, as he is also working on his own project which is in competition with IOTA.
Although IOTA was able to dispel the doubts about security, the matter was not necessarily positive, as there was quite a lot of media coverage of the DCI publications.
Attack on the IOTA Network
In October 2017 there was an attack on the IOTA network. There was the danger that some users could lose their IOTA tokens, because they had previously used their private keys several times. IOTA has therefore decided to store the compromised IOTA itself for the time being. After the attack, a process was set up to allow investors to reclaim their IOTA tokens. However, this caused a lot of resentment among users, as the process took a very long time. In addition, individual IOTA credits were also claimed several times. If this happened, users had to go through a KYC process (Know Your Customer) to get the credits back. Due to the KYC process the delays became even greater. The biggest point of criticism of the whole action is the fact that IOTA simply took the credits of the users and they had to go through a KYC process.
Foundation of the IOTA Foundation
From the beginning it was clear that IOTA would one day be run by a non-profit organisation. Therefore the team has tried to establish a foundation in Berlin. However, as this had not been done before, the process took a very long time. But on November 3rd the time had finally come and the IOTA Foundation was officially recognized. IOTA was the first official crypto foundation in Germany. By March 2019, the IOTA Foundation already had 88 employees.

Due to its headquarters in Berlin, IOTA receives a lot of attention in Germany. However, it should be taken into account that only a part of the staff is based in Berlin. Otherwise, the team is distributed worldwide.
During the crypto boom at the end of 2017 the IOTA price was at times over 5 US dollars. But the situation later normalized and the IOTA price was below 0.25 US Dollar again 1 year later.
Dispute of the founders
That not everything is always going well at the IOTA Foundation became public in August 2018. At that time an internal chat process between the founders (+ Ralf Rottmann) was leaked. The main point is that Sergey Ivancheglo and Serguei Popov complain that they are still not part of the IOTA Board. David and Dominik argue that there has to be a sentence change first and Sergey and Serguei find that they are being held up in return. The chat escalates so violently that it looks as if the IOTA Foundation could break down in the meantime. In the end the founders find each other again and the problems with each other are solved, at least nothing becomes public anymore.
IOTA Technology
While most cryptocurrencies are based on a classic block chain where a new block is attached every few seconds or minutes, IOTA uses the so-called tangle network.
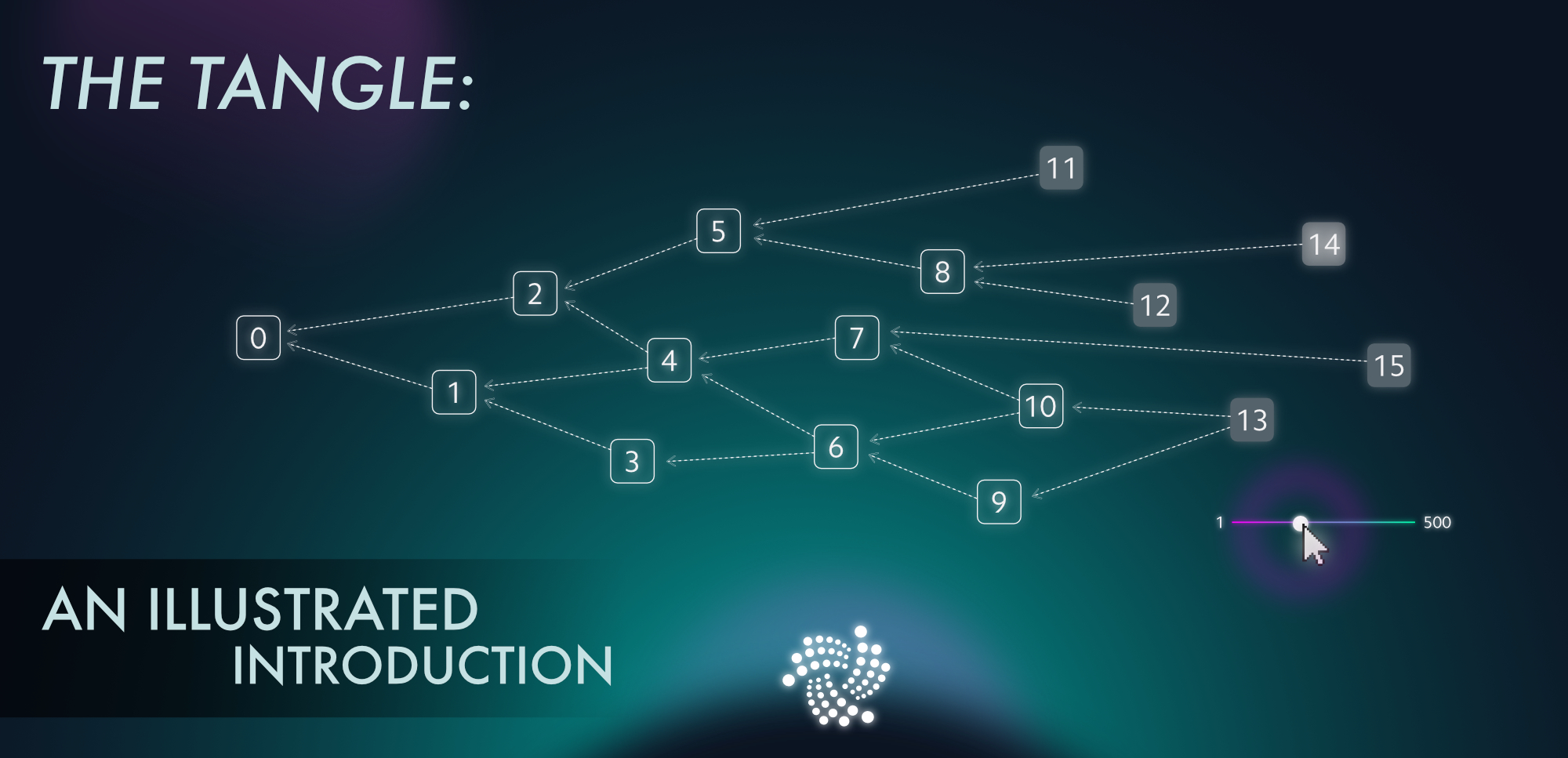
Scalability
Each transaction in the Tangle network can be linked to several other transactions. If you want to execute a transaction at IOTA you have to confirm two more transactions. This works automatically when you make a transaction with the IOTA wallet. The user will not notice this from the outside. Transactions in the IOTA network do not cost any fees, your computer just needs to do some extra work by confirming two more transactions.
This technology also makes IOTA extremely scalable. The more transactions that take place, the more transactions can be confirmed. With IOTA there are also no blocks like Ethereum and Bitcoin, so there is no bottleneck like with a normal block chain, where a new block is only found after a predetermined period of time.
Environmentally Friendly
Also special is the fact that IOTA does not require miners and therefore no energy-intensive mining takes place. Furthermore, all IOTA ever available have already been generated and are therefore available.
In practice it often happens that the tangle network becomes very large. If no action were taken, it would be difficult to operate a node in the network. Therefore, IOTA has regular snapshots. With these snapshots, addresses in the network that do not have a positive balance are deleted. In the long run, snapshots should be done automatically in the network and no longer in the whole network, but rather locally (local snapshots).
Communication between IoT Devices
The fact that there are no fees for transactions is especially practical because machines can easily exchange information with each other without paying fees. Not only IOTA credits can be sent in the Tangle network, but also data via Masked Authenticated Messaging (MAM). Since there are no fees, it can also make sense to send small amounts of money in the network. A fact that is often criticized at Bitcoin, because Bitcoin transactions require too high fees for this.
Resistant to Quantum Computers
Besides the Tangle network and the free transactions, there is much more that makes IOTA special. For example, IOTA is resistant to quantum computers. Although these only exist in the laboratory so far, it is expected that in the future there will be quantum computers that can perform many more operations than today’s computers. Many codes as we know them today could be broken so easily by quantum computers (e.g. Bitcoin). At IOTA this cannot happen.
Ternary System
Apart from the points mentioned above, IOTA distinguishes from other crypto currencies by using the ternary system instead of the binary system. While a number can be represented in the binary system of 0 and 1, the ternary system uses 0, 1 and -1, assuming that the ternary system is more effective for IoT (Internet of Things) devices in the long run. The prerequisite for this is, however, that in future there will be specially developed microcontrollers in IoT devices that use the ternary system. If the hardware continues to be based on the binary system, as is currently the case, this advantage is gone.
Offline transactions
Another special feature of IOTA is the fact that transactions can also take place offline. The prerequisite for this is a node to which the IoT device is connected. This node then stores all transactions that have been carried out and can later, as soon as it is connected to the Internet again, transfer them to the Tangle Network.
34% Attack and the coordinator
It is often talked about crypto currencies that there can be 51% attacks. So if an attacker at Bitcoin has more than 50% of the hashing power in the network, he could effectively determine which transactions come into the block and be confirmed. However, research has shown that theoretically 34% could be enough. This is also true for IOTA. However, the 34% is not a fixed value. It depends more on how much hash power the attacker has and how much of the surrounding nodes he controls. Assuming that an attacker has 40% of the total hash power in the tangle network but hardly controls any surrounding nodes, then the attack will certainly not be successful.
Especially in the beginning of IOTA, where there are still few transactions in the network, this is a central problem. IOTA has therefore introduced the so-called Coordinator. This is basically a central server that confirms all transactions separately. This is to prevent such attacks. The disadvantage is that this solution is centralized and if the coordinator is down or falls victim to a hacker attack, the IOTA network is not usable. That the coordinator is offline and therefore IOTA is not usable has happened in the past.
In the long term the IOTA Foundation is working on finding a way to run the Tangle Network without a coordinator (Coordicide).
Coordicide
 A big problem at IOTA is the coordinator. This is because the whole IOTA network is dependent on this server and the network is not decentralized. On the other hand, the coordinator currently protects IOTA from double spend attacks, for example, where credits are spent more than once. Since IOTA wants to position itself as a decentralized technology, it is clear that the coordinator must disappear from the network in the long run. Furthermore, the IOTA Foundation has a great influence on the network through the coordinator and could, for example, freeze assets or give priority to certain transactions. The plan to remove the coordinator is called coordicide (derived from suicide) by the IOTA Foundation.
A big problem at IOTA is the coordinator. This is because the whole IOTA network is dependent on this server and the network is not decentralized. On the other hand, the coordinator currently protects IOTA from double spend attacks, for example, where credits are spent more than once. Since IOTA wants to position itself as a decentralized technology, it is clear that the coordinator must disappear from the network in the long run. Furthermore, the IOTA Foundation has a great influence on the network through the coordinator and could, for example, freeze assets or give priority to certain transactions. The plan to remove the coordinator is called coordicide (derived from suicide) by the IOTA Foundation.
So far it is not 100% clear how the coordinator will be removed from the IOTA Tangle Network. This is mainly due to the fact that it is not clear which approach will finally replace the coordinator. In IOTA 3 there are discussions about which approaches could replace the coordinator.
- Node Ranking: The idea here is to introduce some kind of ranking or reputation system for nodes. The confirmation of a transaction then also depends on which nodes it was confirmed by.
- Improved Tip Selection Algorithm: This is about where to attach a transaction in the tangle network and which transactions to confirm. An improvement of the existing system could be sufficient to make the coordinator redundant.
- Stars concept: Nodes should be operated by institutions that users trust. These could be governments or companies, for example. The assumption is that they act trustworthily and therefore confirm transactions securely.
Which system will ultimately prevail or whether it will be a mixture of several variants has not yet been decided at this point. What is clear, however, is that IOTA is setting up a test network that does not need a coordinator and in which various assumptions are tested. Because it is not clear what the final solution will look like and what kind of problems will be encountered in the test network, it is not possible to say when the coordinator will be removed from IOTA.
IOTA Addresses
If you have your IOTA not only on a crypto exchange, but actively use it in your own wallet, you should know about the special features of IOTA addresses. An IOTA address can receive unlimited credit. This is also harmless. However, security suffers if credit is sent from an address. As soon as credit has been sent from an address, this address should not be used to receive further credit. The reason for this is that a part of the private key becomes visible when the credit is sent. An attacker could therefore use a brute force attack to gain access to the private key and thus to the credits behind this address.
Let us note: You can receive unlimited IOTA on one address. However, once you have used this address to send IOTA, you should not use it to receive more IOTA.
If you use IOTA’s own Trinity Wallet new addresses are generated all the time, so you don’t have to worry about that. However, if you give out an IOTA address to receive credits, you should be aware of this process. A typical example is an address on a website to receive donations. This should only be used until the funds behind the address are withdrawn for the first time.
Data Marketplace
The data marketplace was presented by the IOTA Foundation in the 4th quarter of 2017. The idea is that it is a central contact point for companies that can sell or buy data there. A typical example is data from temperature sensors that are installed somewhere. These could be made available on the data marketplace and whoever needs them can buy them there. So it could also be worthwhile for the operator to set up the sensor. This does not refer to user data that is to be sold on the platform.
Rather, the marketplace should be used to allow IoT devices to exchange data with each other. The marketplace would then be the central hub with which all devices can communicate. The IOTA Tangle network could also be used for billing for the data that was exchanged. Billing can be done automatically between the machines.

IOTA has already managed to win over 70 companies as participants in the data marketplace.
Qubic
On June 3, 2018 IOTA officially launched Qubic. Although the name was announced in advance and there were many rumours, it was never really clear what Qubic was supposed to be. At the beginning of June there was clarity. Qubic is basically a vision of what IOTA should be able to do in the future. The whole thing can easily be divided into 3 areas.
Smart Contracts: As with other crypto-currencies (e.g. Ethereum) it should be possible to execute Smart Contracts with IOTA in the future. It will then be possible to store certain conditions in the Tangle Network.
Outsourced Computation: Especially in the Internet of Things, devices no longer need to be upgraded to the extent that they can perform certain computing services themselves. Individual computing capacities can also be outsourced. This is exactly where IOTA comes in and promises that in the future it will be possible to outsource computing capacities to the network on the IOTA platform. The respective device can then pay for this with IOTA, for example.
Oracles: Oracles are basically sensors or devices that link the digital world with the real world. The crux of the matter, however, is that one must trust the Oracles and their information.
Qubic was shot very mixed in the scene. Although all IOTA fans were happy about what IOTA should be able to do, it became clear that the points mentioned under Qubic will not be finished for a few years. There is a roadmap to Qubic but no dates or time frames are mentioned. In fact, Qubic generated a lot of hype, but this hype has subsided for the time being, as many points will only be relevant and implemented in a few years.
Units at IOTA
As we explained above, IOTA listed on stock exchanges are often mistakenly referred to as IOTA. Usually MIOTA means 1 million IOTA. So if it is said that the IOTA price is at 0.30 US Dollar it means that 1 million IOTA are currently worth 0.30 US Dollar.
Since IOTA has no decimal places, IOTA can be divided into very small units. How the individual digits in IOTA are called, we have listed in the table below.
| |
|
1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| |
|
1,000,000,000,000 |
| |
|
1,000,000,000 |
| |
|
1,000,000 |
| |
|
1,000 |
| |
|
1 |
Partnerships of IOTA
What IOTA does very well is the acquisition of partnerships. This usually means that the partner does a pilot project based on the IOTA technology. However, this does not mean that the partner does not also deal with other technologies outside of IOTA. At Volkswagen, for example, we know that they are also working on Ethereum and another crypto platform in addition to IOTA.
Among the partners of IOTA are Bosch, Fujitsu, Volkswagen, Cisco, ConsenSys, the government of Thailand, Innogy, REFUNITE, Satoshi Pay and many more.
In the current stage of IOTA, the main goal is to show with the partners what kind of use cases there can be for IOTA. But we are still far away from a mainstream use of IOTA. Everyone should be aware of this.
Criticism of IOTA
The biggest criticism at IOTA is certainly the coordinator. This makes IOTA very different from other crypto currencies, which are much more decentralized. Because through the Coordinator the whole IOTA network is dependent on the Coordinator. If the coordinator goes offline, which has happened in the past, then no transactions are possible in IOTA. In addition, the Coordinator provides a simple point of attack to bring the IOTA network to a standstill.
Even the IOTA Foundation has therefore understood and is focusing on removing the Coordinator from the network. However, to this day there is no one hundred percent certainty that this will ever work successfully. There are different ideas how to make it work, but when they can be implemented and if they can be implemented at all is completely unclear. IOTA with Coordinator will probably not become the standard in the Internet of Things. Of course, IOTA has to be given credit for the fact that the technology and the tangle network is a completely new approach that is very different from other block chain solutions. If you go this way you will always have problems in the beginning. But this also creates a certain risk, which you should be aware of when making your investment.
Besides the coordinator, the argument between the founders has not exactly created trust. In the founders’ chat, the dissolution of the IOTA Foundation was discussed. Sure, there are problems everywhere, but you rarely experience such massive problems in other projects. After all, this is about a crypto currency and a project that was worth several billion US dollars at times.
Everybody should be aware that IOTA still has a long way to go and a lot of things are still uncertain. In addition, there are many partnerships that IOTA has initiated, but that does not mean that the partners will use IOTA in the long run. Volkswagen, for example, is a frequently mentioned partner of IOTA. But it is also known that Volkswagen is not only involved with IOTA, but also with other solutions such as Ethereum.
As the IOTA Foundation is based in Germany, there are sometimes very exuberant reports that IOTA is becoming the standard in the Internet of Things. But IOTA is still far away from this. It is also noticeable that IOTA is much less hyped in some countries than in Germany. In the USA IOTA has hardly played a role so far.
It is often said that transactions are free of charge, in the end the user pays for one transaction with electricity and computing power he needs to confirm two more transactions. It is not necessarily better for security that individual users confirm transactions. In the end, time will tell if the IOTA approach is the right one.
As with most other crypto currencies, there are no real applications where IOTA plays a role, apart from a few pilot projects.
Conclusion
Who invests in IOTA should be aware that it is a risky crypto investment. IOTA may well become the standard in the Internet of Things, but it may just as well happen that IOTA disappears from the scene again at some point. The team has an ambitious plan but also still a long way to go. So far it is not clear if it will be possible to remove the coordinator, even though they are working hard on it.
Furthermore, it is necessary to convince as many companies as possible that IOTA will become the standard in the Internet of Things and that they will adapt the technology. The current partners are a good start but everyone should be aware that these are pilot projects. We are still far from a broad adaptation of IOTA.
Personally, I would only invest a small part of my crypto portfolio in IOTA, if at all. Nevertheless IOTA has a good chance to become successful.
IOTA Wallet
If you do not want to leave your IOTA on a crypto exchange, you can store it on your own software wallet. IOTA offers the Trinity Wallet developed by the IOTA Foundation.
The safest way to store your IOTA is the combination of the Hardware Wallet Ledger Nano S and the Trinity Wallet.
Since IOTA is not based on a classic block chain, most general wallets that can hold multiple crypto currencies do not offer IOTA integration. For security reasons alone, we recommend using only the Trinity wallet (ideally with the ledger Nano S).
IOTA Seed explains
It is important to know that IOTA has a seed. This is an 81-digit code that gives you access to your IOTA credits. The Seed is similar to the Private Key at Bitcoin. However, in the past the normal IOTA Wallet could not generate a Seed. Since some users didn’t want to think up an 81-digit code, they looked for seed generators on the Internet. But some of them were manipulated and they saved the generated seeds. Later on, the credits of the unsuspecting users were stolen. So you should always be aware of the fact that the owner of the seeds can dispose of the credits at any time. So be careful how you generate the seeds and where you store them.
A typical IOTA Seed may look something like this: PNBLOZHTAJUNNFOVRNNGCMYCGADIBVVADHXZYCJQPKDEHZKRCBVWNBNBCFQXC9LWUBRCDIKKRVUQJGPWL
There is the requirement that the seed must be at least 81 digits long and must contain at least a 9.
IOTA Buying and Selling
If you just want to buy IOTA for Euro you can do that at eToro. On the platform you can also simply deposit Euro or USD by credit card, PayPal or bank transfer. IOTA is also traded at Binance, the world’s largest crypto exchange. There IOTA is only traded against BTC, ETH or BNB. To buy IOTA there you have to buy BTC from another platform (e.g. Coinbase) and send it to Binance.
IOTA Course and Price
Here you will find the current exchange rate at which you can buy IOTA and get an insight into the exchange rate development of the crypto currency.
Links
IOTA Foundation: IOTA.org
Wallet: Trinity
Tangle Explorer: TheTangle.org